Lupus is a chronic, autoimmune disease that occurs when the body starts fighting against its own cells, causing inflammation, pain and swelling. It can affect any part of the body, from the skin to the heart. It can be very difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are similar to those of other ailments.
Friends and family may have a hard time understanding the disease, as its symptoms are not visibly apparent and can range from mild one day to severe the next.
What causes lupus?
Lupus may be caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
“Patients who have a family history of lupus may have a 25% to 50% chance of getting lupus, because their genes may be damaged,” explains rheumatologist Javeria Bhawal, M.D. “These damaged genes transfer from the mom to the kids. And these kids are more prone to have lupus.”
Other common triggers for lupus include:
- Viruses: having an infection
- Ultraviolet light: exposure to sunlight
- Medications: certain medications, especially sulfa
Lupus is more common among African Americans and Hispanics. And though it primarily strikes women, men can acquire the disease as well. Lupus is considered a young person’s disease, as most cases are diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 50 years of age.
Common symptoms of lupus
Lupus can affect any part of the body, but common symptoms include a butterfly-like rash on the face, hair loss and joint pain with swelling in the fingers.
The following diagram shows other areas of the body that can be affected by lupus.
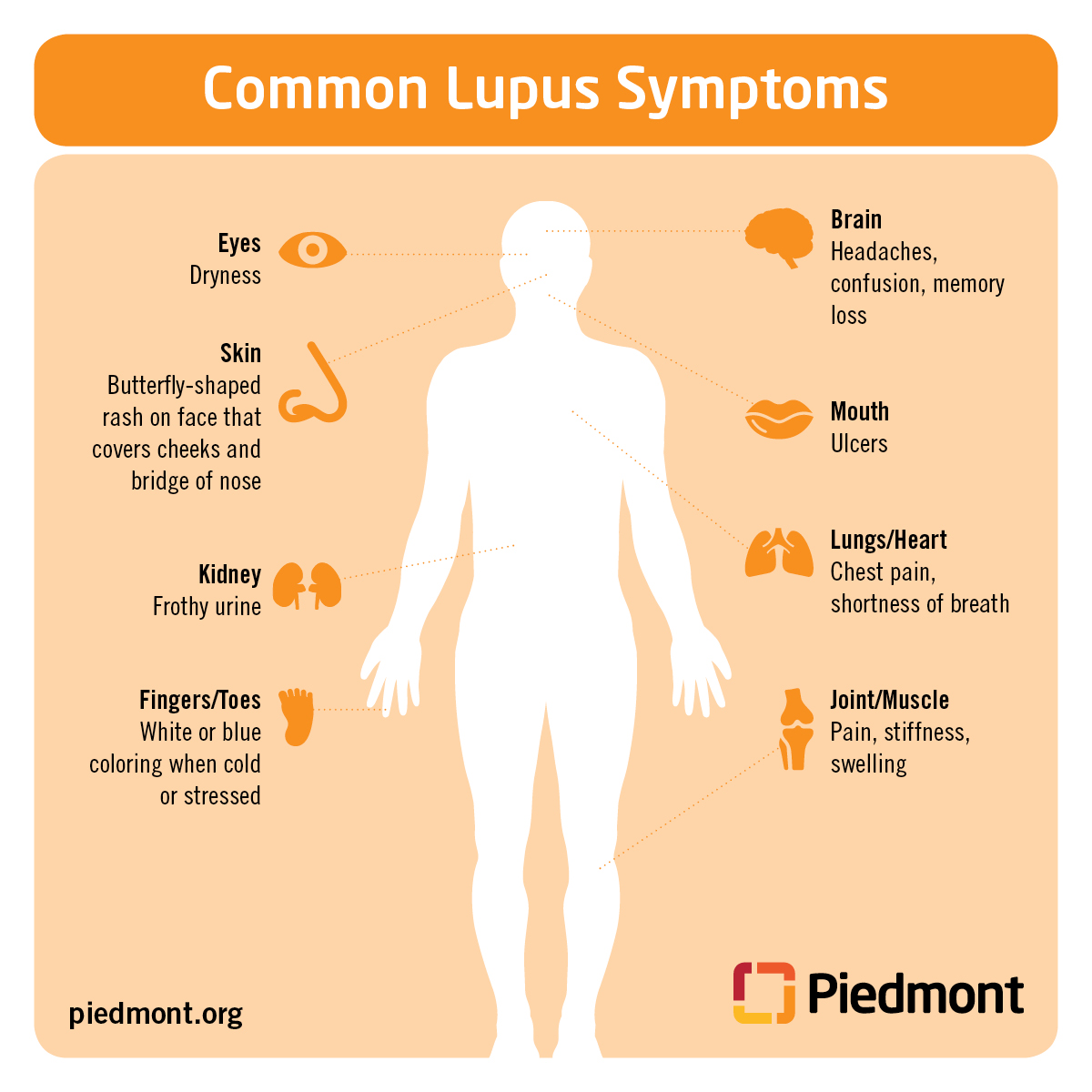
Lupus can go into remission, but patients often experience ‘flare-ups,’ or episodes where they have a return of their symptoms.
“The most common trigger (for a flare) is the sunlight,” Dr. Bhawal says. “Another is infection, especially in the cold weather if (someone with lupus) gets a cold or flu, it may trigger lupus. At times, different drugs can trigger these flares, and at times just anything can trigger the lupus flare.
How is lupus treated?
Treatment for lupus depends on the symptoms and the area of the body affected by the disease. Common treatments include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: These drugs include Aleve and ibuprofen to treat pain and swelling.
- Antimalarial drugs: Antimalarial drugs can help improve muscle and joint pain, skin rashes, and other symptoms such as fatigue and fever.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids help decrease swelling, tenderness and pain associated with inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressants are used to control inflammation and an overactive immune system. Some were developed as chemotherapy drugs.
Coping with lupus
There is no cure for lupus, but there are some healthy ways to manage the disease. Dr. Bhawal offers the following tips:
- Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 50 or higher and wear protective clothing when exposing yourself to the sun.
- Eat a low-fat diet to control your BMI.
- Stay as active as possible to avoid weight gain.
- Always take your medicine and continue to follow up with your doctor.
Need to make an appointment with a Piedmont physician? Save time, book online.